Efficient DNA-based data storage using shortmer combinatorial encoding
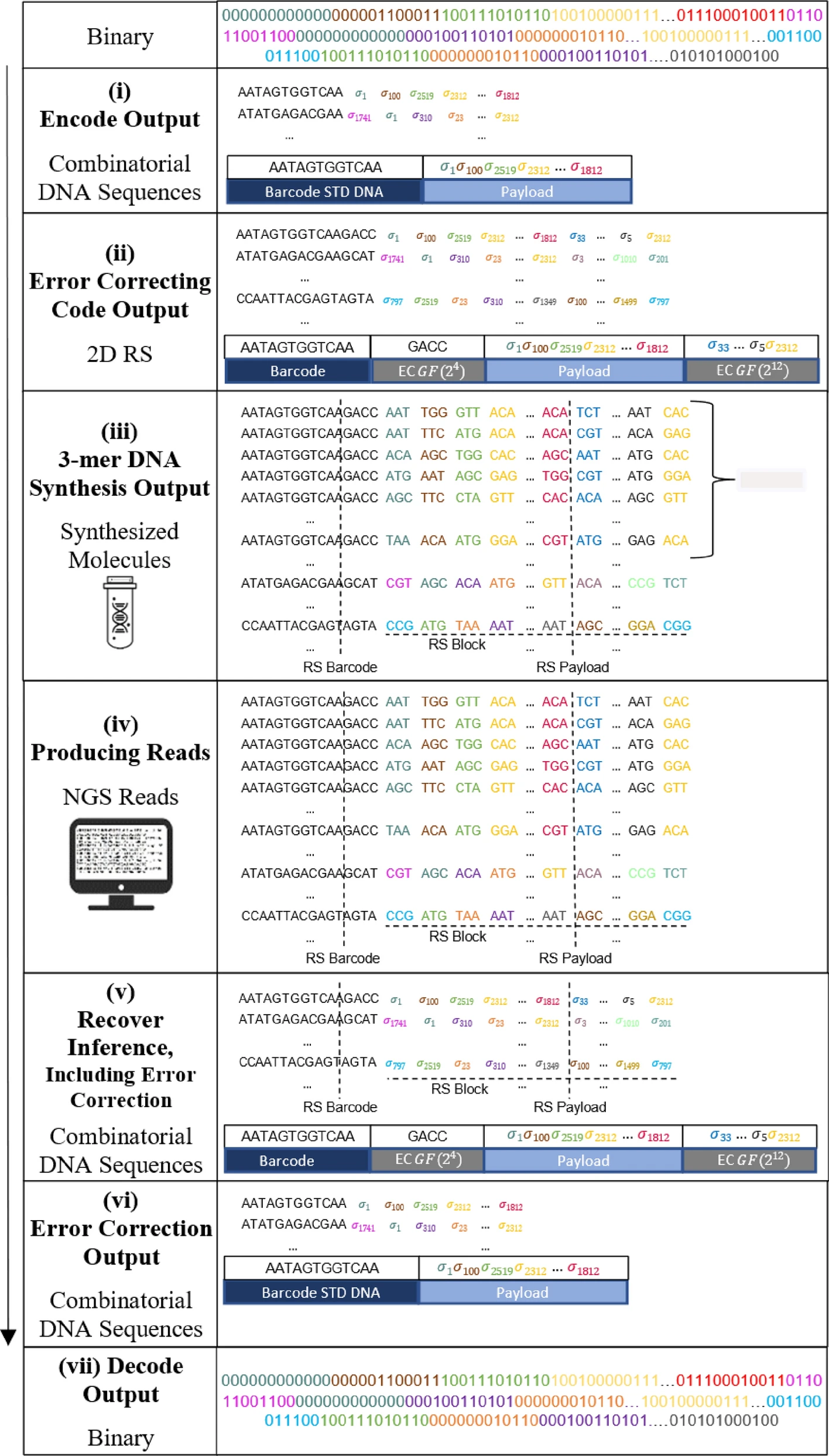
DNA data storage offers compact, durable archival solutions, with composite DNA alphabets enhancing logical density. This paper presents a new combinatorial encoding method, achieving up to a 6.5-fold increase in storage density with near-zero reconstruction error. Using distinct DNA shortmers to create large alphabets, each letter comprises a subset of shortmers, enabling efficient information encoding. We formalize combinatorial schemes, analyze properties like information density and reconstruction probability, and design an end-to-end storage system, integrating 2D error correction. Simulations show 2D Reed-Solomon codes significantly improve reconstruction, confirmed by successful combinatorial synthesis experiments, underscoring the approach’s robustness and potential.
Sequencing Coverage Analysis for Combinatorial DNA-Based Storage Systems
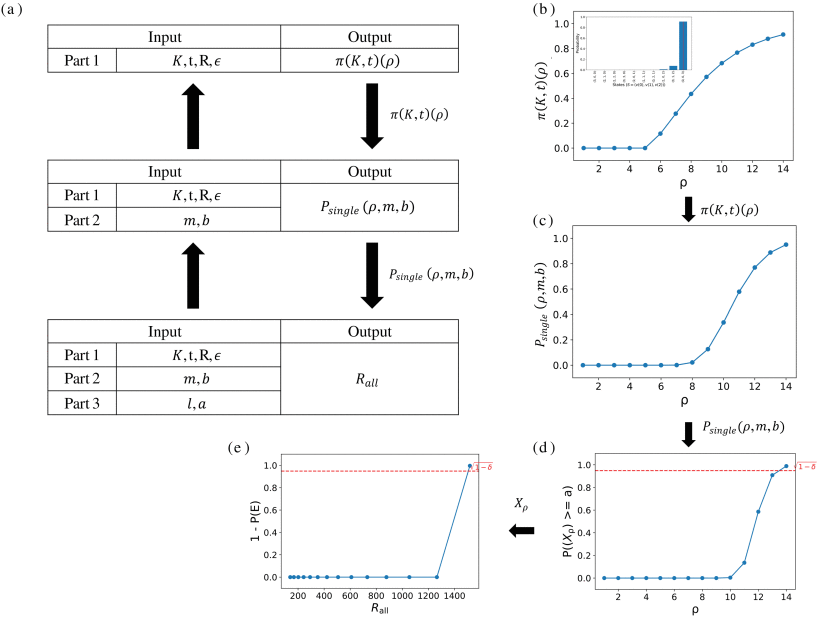
This study introduces a model for determining the required sequencing coverage in DNA-based data storage, focusing on combinatorial DNA encoding. It uses a variant of the coupon collector distribution and a Markov Chain representation to characterize the distribution of sequencing reads needed for error-free message reconstruction. Theoretical bounds on decoding probability are developed and validated through simulations. This work provides insights into sequencing coverage, decoding complexity, and error correction. Additionally, a Python package is offered to compute required read coverage, based on code design, message parameters, and a desired confidence level.
Error-Correcting Codes for Combinatorial Composite DNA
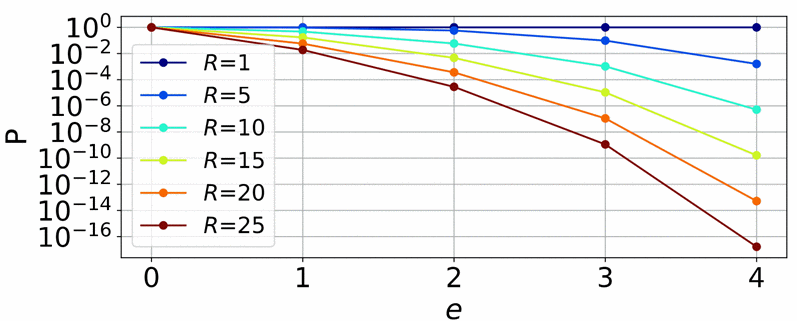
DNA data storage is emerging as a potential solution for archival data, with the combinatorial composite DNA synthesis method extending its capacity by using short DNA fragments, or shortmers, as building blocks. However, missing shortmers during reading can cause symbol errors. This paper models these as asymmetric errors and proposes error-correcting code constructions with a lower bound on redundancy, providing an encoder and decoder for this setup. The error model is supported by experimental data and includes a statistical evaluation of error probability based on read depth.








